

Virtual, mixed, augmented and extended reality, do you know the difference between each of them and their specific use cases? When you’re just starting out learning about the different virtual technologies it can be confusing defining what’s what, which is why we’ve created this blog post.
We’ll clearly explain each technology so you can fully comprehend what they are and when they can be used so you can harness their full potential. So, first a brief explanation of each…
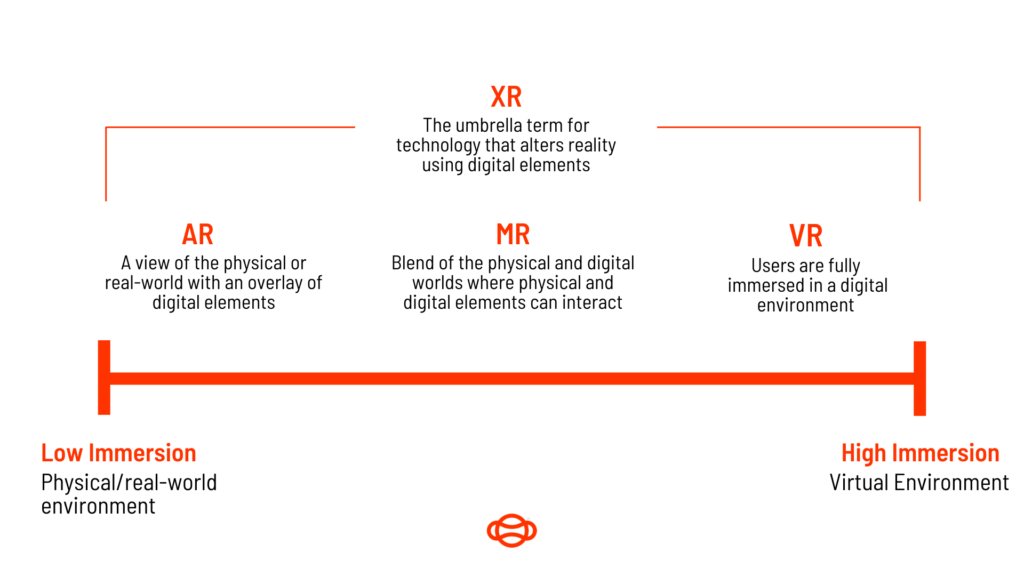
XR, VR, MR and AR: Definitions
Extended Reality (XR)
Extended reality is the umbrella term for any technology that alters reality using digital elements to create real-world environments. Virtual, mixed and augmented reality are all different types of extended reality.
Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual reality is when you interact with a fully immersive digital environment using a VR headset. Headsets will generate realistic sounds, images and other sensations that transport you to a completely different reality.
On the spectrum of user immersion, VR platforms are considered high immersion, because users feel as though they’re fully immersed in a different world. It’s heavily used in the world of gaming, but also has wide applications for enterprises wanting to train and upskill their employees.
Many industries are using VR for health and safety-based training and hazard recognition, where staff can enter virtual worlds and recognize hazards in a range of environments from warehouses, substations, workshops and construction sites.
Mixed Reality (MR)
Mixed reality, or hybrid reality as it’s sometimes referred to, is a blend of virtual and augmented reality, helping to produce visualisations where the physical and digital interact together in real time.
Mixed reality devices gather information about our surroundings and seamlessly place information and content within that space so users can interact with it. Unlike VR, users can still interact with their physical space, placing it in the middle of high and low immersion.
Mixed reality training works extremely well in manufacturing training environments where engineers can receive and act on information and instructions in real time relating to components through an MR headset, helping to increase accuracy and speed when working on assembly and maintenance.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented reality uses our existing environment and adds elements to it using a screened device, mobile and tablets are the most popular mediums that utilize AR. AR is considered low immersion as users are still very present in their physical world.
AR Snapchat and PokemonGo are great examples of augmented reality, where elements exist simultaneously with our physical reality.
What’s the difference between augmented and mixed reality?
Augmented reality is simply a view of the real world, with an overlay of digital elements. Mixed reality offers the same concept, the real world with an overlay of digital elements but with mixed reality, this goes one step further and the physical and digital elements can interact with one another. Mixed reality sits nicely between AR and VR on the immersion scale.
Now you know the different types of virtual technologies, we can explore them a bit further…
A brief history of XR technology
People think that XR technologies are a new phenomenon, however the origins of XR technology can be traced all the way back to the 1800s when scientist Charles Wheatstone outlined the concept of stereopsis, where the brain combines two images from each eye to make a single 3D image.
This led to the development of stereoscopes and stereoscopic displays are a key part in today’s VR systems to bring depth to digital images that enhance immersion.
The 1950s, 60s and 70s brought us a range of new VR and AR innovations in action from the Headsight headset to computer generated tours of the streets of Aspen.
From the 1980s to 2000 VPL Research were the first company to sell VR goggles and gloves and co-founder Jaron Lanier, coined the term ‘virtual reality’ in 1987. VR gaming devices like the SEGA VR-1 came to market, along with affordable VR headsets for home use. In 1998, the NFL brough AR to the sports broadcasting industry with the lines overlayed on camera feeds.
From 2010 onwards the momentum of XR technologies rapidly increased with the Oculus Rift, key tech players Sony, Samsung and Google launching VR and AR devices, the introduction of the HoloLens, PokemonGo bringing AR into the mainstream and AR making appearances in mainstream retail.
Today, we’re seeing VR, AR and MR be utilised by industries globally, we’ll explore these later in this article, but the widening application of XR is testament to its growth and applicability to enhance aspects of our daily lives.
Why are people using XR technology?
Every industry can benefit from XR in some way but the industry’s leading the adoption of XR technology are engineering and manufacturing, retail and consumer and professional services with learning and development being one of the most prevalent uses and with so many benefits, it’s easy to see why…
· VR platforms offer a high amount of learner engagement for all different types of learners, improving learner retention and recall.
· There is much less risk involved in virtual reality environments.
· The cost savings from using XR training are significant through remote training and eliminating the need for factory and site shutdowns.
· It takes less time to learn with VR training, and results in fewer mistakes.
· VR can attract the best job candidates because it shows business prioritize innovation and employee development.
· Training can be tracked to evaluate the effectiveness of the VR training.
Want to explore these benefits in depth? Head over to our VR Training in the Workplace: What are the benefits? blog.
What industries are using XR and how are they using it?
Aviation
XR has a wide range of applications for safety and maintenance in the aviation sector. Using VR aviation training, staff can practice aircraft maintence procedures, practice repairs and improve their ability to identify and repair any hazards on aircraft materials as well as engage in flight deck training, cabin crew training and aircraft inspection training to ensure the safety of passengers and crew.
Automotive
XR technology is great for onboarding for automotive factory environments where most new members of staff typically learn specific operational procedures by shadowing an experienced operator.
By building a virtual digital twin of the factory and the different lines and equipment within it, staff can immerse themselves and train virtually.
The result? When trainees visit the site for the first time, they’re already familiar with the different types of equipment and operating procedures. Customer using interactive digital twins for VR automotive training are seeing a 50% reduction in on-the-job training and can drastically increase the number of staff members being trained at a single time.
Energy, Oil and Gas
There are a whole host of safety use cases in the oil and gas industry that users can train for in VR such as welding, working at heights, working in confined spaces, fire safety, machinery operation and PPE safety to name a few. By using VR energy training, users can head out into the field confidently and perform these procedures with reduced risk and error.
Recommended Reading: How VR can be used for Safety Training in the Oil and Gas industry
Medical
With people on the receiving end of medical procedures, the treatment and equipment they encounter must be of utmost safety. XR training in the medical industry means that medical professionals can practice and perfect complex procedures in risk-free environments, enhancing the quality of care for patients.
It’s not just medical professionals who can benefit from VR medical training, biomedical engineers who work on equipment like electro-cardiovascular, ventilation, anaesthesia operating theatre and MRI equipment can also benefit from maintenance and repair training in VR.
Military & Defence
Military and defence are extremely high intensity environments, where each and every move can have consequences and therefore mastering procedures and safety training is paramount. XR training can be used in the military and defence sector across a range of scenarios:
· Medical Training: VR medical training can be utilised to prepare medics for battlefield medical procedures that require quick and urgent care.
· EOD Training: The significance of EOD training can be hard to replicate in real-life, but VR can be used to simulate the identification, handling and disposal of explosive devices.
· Equipment and Vehicle Simulations: Crews can practice operation, manoeuvres, fire drills and communication in a realistic virtual environment with XR.
Food and Beverage
The food manufacturing industry must meet strict safety and quality standards and therefore training and staying up to date with these requirements is crucial.
XR training is perfect because it provides realistic simulations to train employees in a range of scenarios:
· Equipment Operation and Maintenance: MR and VR training can be used to train employees how to maintain and repair food processing machinery by practicing troubleshooting, learning the correct assembly and disassembly of machinery and gaining familiarity with equipment and their controls.
· Quality Control and Inspections: VR scenarios can be created to help employees identify defects, practice quality control protocols and learn about specific inspection criteria.
· Food Hygiene: Factories need to carry out regular audits and swabs for pathogens such as Salmonella and Listeria. Traditionally this is a manual paper-based exercise and open to error. When working with a client we provided hands free operation that meant users could carry out swabs and accurately map the location using the HoloLens 2 device.
The results of swab where then overlaid on to a real-time digital twin of the facility and if swabs did come back positive, users were guided to the correct location using holographic wayfinding to begin the cleaning process.
Construction
Construction sites can be one of the most fatal environments for employees, with increasingly stringent safety procedures. Getting staff to take safety seriously is crucial in this sector. VR construction training provides an effective, fun and trackable method of safety training, ensuring workers physically carry out the training that they’ll be doing on-site. From working at heights, confined spaces, line and equipment opening and more there are a range of options for safety training in VR.
Pharma
With a range of complex and high precision processes in pharma manufacturing, failure to comply with processes or even the loss or contamination of products can cost companies hundreds. VR pharma training can be used to streamline the pharmaceutical manufacturing processes and medical device packaging processes as well as improve safety through risk and safety training.
Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry can hugely benefit from XR training and because it enables staff to perform faster maintenance and repairs, training in a safe-risk free environment, collaborate with others from anywhere in the world helping to improve efficiency and keep equipment and machinery operating at optimal efficiency.
The powerhouse combination of digital twins and XR training
With a background in 3D laser scanning, at Luminous we have the ability to quickly and efficiently digitise your plant to create an accurate real-time 3D digital twin. Once we have the 3D model, standard operating procedures can be replicated.
Staff can meet up virtually in the 3D version of your facility and can be taken through the required training, reducing the need for inductions and permits to work which can be time consuming, and allows then to train in a safe, repeatable environment.
What XR hardware is available?
As time goes on, there are so many options for VR, MR and AR devices, so here are some of the key devices for each type of technology:
· Virtual Reality: MetaQuest, Apple Vision Pro, Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, Pico VR
· Mixed Reality: Microsoft Hololens, Windows Mixed Reality Headset
· Augmented Reality: Rayban and Meta Wayfarer Smart Glasses, Google Glass, Mobile Phones, Tablets
How is XR content created?
You might have engaged with XR content before, but are you aware of how XR content is created? Creating the content for XR requires a combination of skills, software and hardware such as programming skills in a specific language and familiarity with XR development platforms like Unity or Unreal.
60% of AR/VR content is made using the Unity games engine and with good reason, Unity supports a range of immersive experiences and offers a range of tools, asset libraries and real time rendering capabilities.
How long does it take to create VR content?
Creating an incredible VR training experience takes time and this can be different depending on the complexity and scope of the project. A simple VR environment with basic functionality can be done in a couple of weeks or take months. Highly detailed VR experiences can take 6 months or longer.
This is because there are so many things to consider when creating the content such as the platforms the content will be used on, creating visual assets and artwork, the interactivity of the scenario and creating scenarios for multi-user purposes which can increase development time significantly.
There are tools on the market however, that allow XR content to be created much faster than usual. Our visual scripting tool for Unity, FLOW means XR content can be created 80% faster than usual for skills training and development.
The Future of XR
An industry that’s been evolving since the 1800s, the growth of XR technology will continue to grow and with more technology becoming available to the masses it will only become easier to reap the rewards and see the technology extending to more and more areas of our daily lives. 91% of business organizations are already leveraging or planning to adopt VR/AR technology.
Can you see VR training becoming part of your business? Why not chat to one of our experts over a coffee and learn more about VR for the various sectors and see how it could potentially work in your business.
Interested in getting the latest VR, MR and AR news straight to your inbox? Sign up to our newsletter…